Topic Name:
Evaluating the Impact of Digital Transformation on Organizational Performance and the Integration of Sustainable Practices in India's Marine Industries
Acronyms of Topic Name- NA
Visual Abstract Image
Objectives
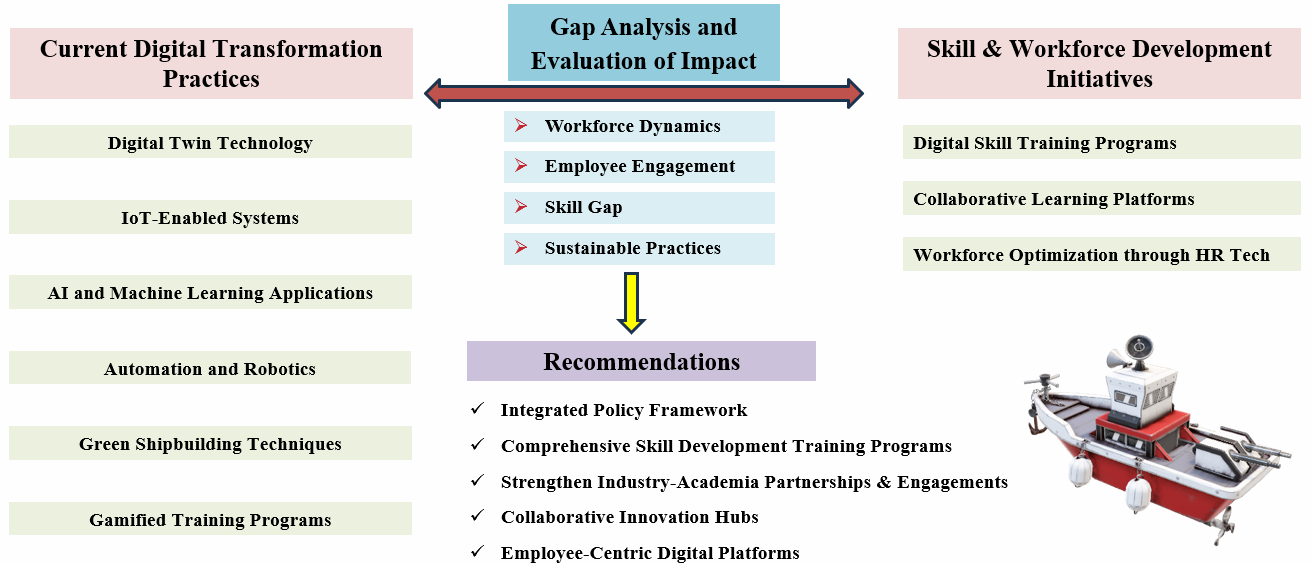
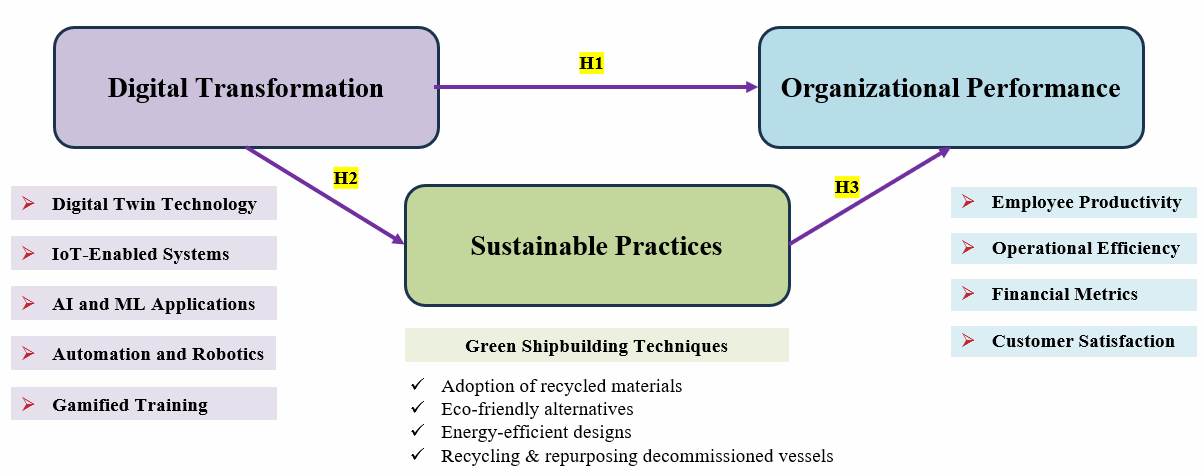
- Evaluate Digital Transformation Strategies - Analyze the adoption and effectiveness of digital transformation practices in India’s shipbuilding, ship-repair, dockyards, and marine industries, identifying key drivers and barriers to implementation.
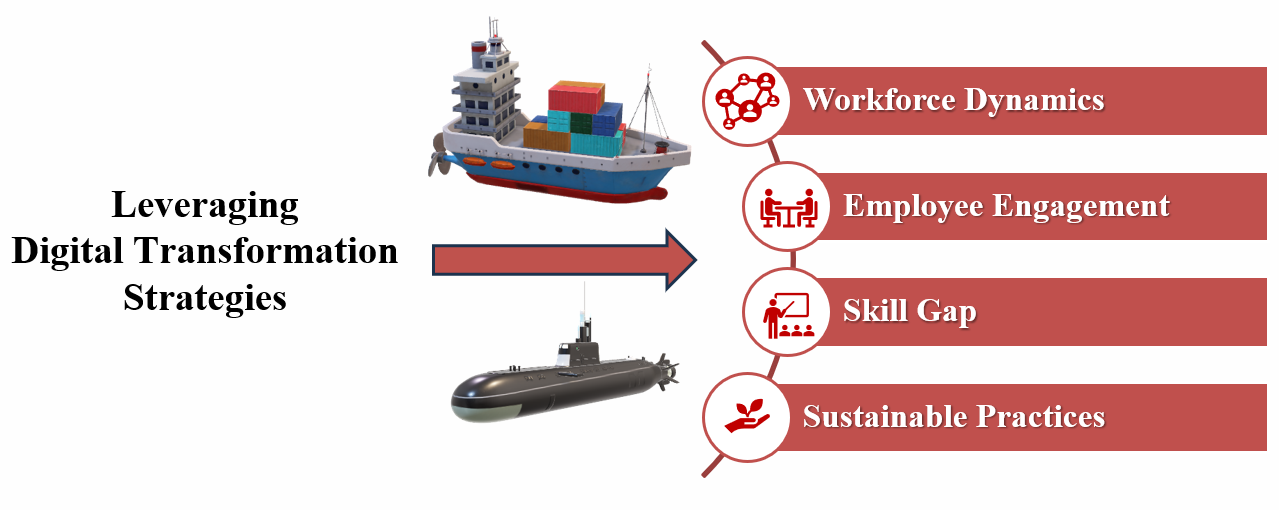
- Enhance Workforce Dynamics and Skill Development- Investigate the impact of digital tools on workforce engagement, employee dynamics, and skill gap reduction, proposing frameworks to enhance human capital within the marine sector.
- Align Marine Industry Practices with Sustainability Goals- Assess the integration of sustainable development objectives in digital transformation strategies, emphasizing the industry's role in promoting environmental responsibility and long-term ecological balance.
- Develop a Comprehensive Roadmap for Industry Modernization- Design a strategic roadmap for creating a resilient and efficient Indian marine sector that leverages digital tools and sustainable practices to achieve global competitiveness and alignment with international standards.
- Provide Actionable Insights for Policy and Industry Adoption- Deliver actionable recommendations for policymakers and industry leaders on harnessing technology and sustainability to modernize the marine sector and ensure its growth and innovation in a globalized economy.
Issues Involved
India's shipbuilding and repair industry, spanning 7516.5 km of coastline, includes 27 private firms, 8 public units, and 45 dry docks, employing over 28,000 workers. Despite manufacturing 1153 vessels in three decades, the sector struggles with digital transformation, limiting technological progress, sustainability, and global competitiveness. Addressing these challenges is crucial for fostering innovation, aligning with environmental goals, and building a resilient, future-ready maritime industry that meets modern economic and operational demands. Key issues to be addressed included in the scope of the project are:-
- Workforce Skill Gaps. The rapid adoption of digital tools requires a workforce skilled in advanced technologies such as automation, AI, and IoT. However, many workers lack digital proficiency, hindering operational efficiency and innovation.
- Resistance to Change. Employees and management often resist adopting new technologies due to fear of redundancy or a lack of understanding. This resistance can stall the digital transformation process.
- Employee Engagement and Morale. Transitioning to digital workflows can create uncertainty and affect employee morale, leading to disengagement. Low engagement can reduce productivity and increase turnover.
- Leadership and Change Management. Leaders in these industries may lack the skills to manage digital transformation effectively, and poor leadership can derail transformation initiatives.
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy. Increased reliance on digital tools and data exchange raises vulnerabilities to cyberattacks. Breaches can disrupt operations and compromise sensitive information.
- Environmental and Sustainability Compliance. Digital transformation often overlooks sustainability, resulting in non-compliance with green regulations and practices. Non-compliance can lead to penalties and environmental degradation.
- Workforce Redundancy and Unemployment. Automation and digitalization can lead to job redundancies, particularly for manual labor roles. Workers' displacement can result in social and economic challenges.
- Integration of Traditional Practices with Technology. Combining traditional shipbuilding practices with modern technology can be challenging due to cultural and operational barriers. Inefficient integration can slow down productivity and innovation.
- Inadequate Infrastructure for Digital Tools. Many facilities lack the infrastructure to support advanced technologies, such as high-speed internet or automated systems. Poor infrastructure hampers the successful implementation of digital solutions.
- Sustainability in Resource Utilization. Shipyards and dockyards consume significant resources, and digital transformation must focus on minimizing waste and improving energy efficiency. Unsustainable practices can exacerbate environmental damage and increase operational costs.
Team Lead
Name: Dr Debasis Dash, Associate Professor (HR & BS/OB)
Email ID: debasis.dash@nmims.edu
Team Member (1)
Name: Dr Abhay Kumar, Associate Professor (Finance)
Email ID: abhay.kumar@nmims.edu
Team Member (2)
Name: Dr Shalini Wadhwa, Assistant Professor (Gen. Mgmt.)
Email ID: shalini.wadhwa@nmims.edu



